 IN DETAIL AND BY REGION OR PURPOSE IN DETAIL AND BY REGION OR PURPOSE
 See also: Legal Information about EUCLID See also: Legal Information about EUCLID
EUCLID is an international intergovernmental organization holding a university charter. It was established by intergovernmental agreement under public international law, registered with and published by the United Nations, with explicit governmental and intergovernmental accreditation.
For this reason, the United Nations Secretariat letter of December 2012 makes reference to 5 institutional belonging to this categorization of "Regional / International Institutions," namely: (1) European University Institute (2) IMO International Maritime Law Institute (3) United Nations University and (4) World Maritime University, in addition to "EUCLIDE (Pôle Universitaire EUCLIDE)" which is the official listing name in French.
Regarding accreditation, the defining agreements clearly state:
In order to ensure the international usefulness of the programs offered, EUCLID is chartered to confer diplomas, degrees and completion certificates accredited by the ministries of Education of the Participating Parties. (Article 1)
Hence, the certificates and degrees granted by EUCLID are governmentally chartered and accredited, which facilitates global recognition because all UN Member States participate in the UN Charter Article 102 processes as a common means to validate treaties.
Furthermore, the headquarters agreements (entry into force, March 2011 for C.A.R.; entry into force June 2013 for Gambia) specifies:
This Agreement, governed by international law... will be also communicated... to the United Nations - UNESCO / IAU for the registration of EUCLID to the international directory as accredited institution having an academic nature and having intergovernmental status. (Article 13)
The governments that have granted MOE accreditation under international law to EUCLID are listed below in alphabetic order, and the intergovernmental agreement containing the accreditation clause is registered and published by the United Nations Treaty Section in accordance with Article 102 of the UN Charter.
| Government / MOE |
Region |
Document |
| Burundi |
Africa (UNESCO convention applies) |
 |
| Central African Republic |
Africa (UNESCO convention applies)\ |
 |
| Comoros |
Africa / Indian Ocean region |
 |
| Gambia |
Africa |
 |
| Saint Vincent & Grenadines |
Americas / CARICOM region |
 |
| Senegal |
Africa (UNESCO convention applies) |
 |
| Sierra Leone |
Africa |
 |
| Timor-Leste |
Asia / ASEAN region |
 |
| Uganda (MOU) |
Africa (UNESCO convention applies) |
 |
| Vanuatu (MOU) |
Australia-Pacific region |
 |
Below, this page also discusses recognition of accreditation granted by other intergovernmental organizations, as well as the issue of accreditation in the United States and other specific regions.
 See also Legal Documents See also Legal Documents

 BY REGION BY REGION
 Information for Region 1A (Africa) Information for Region 1A (Africa)
EUCLID is full member of the Association of African Universities which ensures recognition throughout the continent.
In Africa, legal recognition is also governed by a UNESCO-registered convention  which applies to EUCLID degrees in the following 22 countries (21 in Africa proper + Holy See): which applies to EUCLID degrees in the following 22 countries (21 in Africa proper + Holy See):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- United Republic of Tanzania
|
|
For more information, please contact the Ministry of Education of your country of residence and/or prospective employment.

 Information for Region 1B (Europe, Middle-East) Information for Region 1B (Europe, Middle-East)
In Europe, EUCLID is treated as a public and accredited non-EU institution. For more information, please contact the ERIC - NARIC center in your country of residence and/or prospective employment. All EUCLID programs are compliant with the standards set forth in the Bologna process documents (which includes the use of ECTS), and a diploma supplement is issued upon request.
In the Middle-East, international education generally relies on the UNESCO-IAU handbook for recognition. For more information, please contact the Ministry of Education of your country of residence and/or prospective employment. The EUCLID - ICCI agreement is also of importance in this context since most Middle-Eastern countries are also OIC/ICCI Member States.

 Information for Region 2 (United States) Information for Region 2 (United States)
The United States is rather unique in that it has no federal Ministry of Education or other centralized authority. By contrast, in the vast majority of countries, accreditation is granted by the Ministry of Education, and this is how EUCLID is accredited.
In the United States, the US Department of Education has recognized certain accredited body whose judgment is deemed reliable to certify a certain level of educational quality.
It should be understood that EUCLID is not a US-based institution and does not seek or hold accreditation from CHEA-related agencies (CHEA is the Council for Higher Education Accreditation). However, CHEA considers the International Association of Universities as the "International Quality Assurance Agency" of reference  , and we have documented above that EUCLID is duly listed in the UNESCO-IAU handbook. , and we have documented above that EUCLID is duly listed in the UNESCO-IAU handbook.
From a US perspective, EUCLID is a non-CHEA accredited foreign institution. EUCLID students who desire to use their EUCLID degree in the United States will first have their education evaluated by a 'foreign credentials evalutors' such as WES or NACES member private agencies. EUCLID provides extensive institutional and academic documentation to students who may need to accomplish this process.
Since 2007, EUCLID has worked with various US state agencies, bearing in mind that EUCLID does not consider its programs to be alternative to CHEA-accredited program for US residents, and aware that among the 50 states unique regulations may apply. As of 2013, among these 4 specific states, Michigan and Maine have completed their review procedures, but Oregon and Texas are still pending.
Applicants residing in jurisdictions were special regulations or restrictions apply may not apply for EUCLID programs as a matter of permanent policy.
For employment with government bodies, the UNESCO-IAU listing is deemed sufficient for a number of US states but not by others. This listing is also sufficient and necessary for acceptability by the US Citizenship and Immigration Service.
Students who are seeking a program specifically requiring CHEA-related accreditation (or in some cases only regional accreditation) should consult http://www.chea.org/search/
Students who are seeking more information about international / foreign education evaluation may consult http://www.foreigncredits.com/Default.aspx
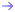 List of accepted countries and states of residence for EUCLID applicants List of accepted countries and states of residence for EUCLID applicants
 List of non-accepted countries and states of residence for EUCLID applicants List of non-accepted countries and states of residence for EUCLID applicants
For more information about international education from a US perspective:
 Accreditation in the United States (official) Accreditation in the United States (official)
 Distance Education: How to Protect Yourself and Make a Wise Investment Distance Education: How to Protect Yourself and Make a Wise Investment
 Consumer Fraud Reporting (USA) Consumer Fraud Reporting (USA)

 Information for Region 3 (Americas excluding USA) Information for Region 3 (Americas excluding USA)
EUCLID is directly accredited by one ministry of education in the region. For more information on the validation of international education in your specific case, please contact the Ministry of Education of your country of residence and/or prospective employment.
 Information for Region 4 (Asia / Pacific) Information for Region 4 (Asia / Pacific)
EUCLID is directly accredited by two ministries of education in the region. For more information on the validation of international education in your specific case, please contact the Ministry of Education of your country of residence and/or prospective employment.

 OTHER INTERGOVERNMENTAL AGREEMENTS PERTAINING TO EUCLID ACCREDITATION OTHER INTERGOVERNMENTAL AGREEMENTS PERTAINING TO EUCLID ACCREDITATION
EUCLID's academic accreditation is recognized and reaffirmed by the following intergovernmental organizations:
- ICCI (Islamic Chamber of Commerce and Industry), an affiliated organ of the Organization of the Islamic States
- ECOWAS, a 15 Member State regional organization
- CAFRAD, a 36 Member State specialized organization

 Regarding CAFRAD: Regarding CAFRAD:

EUCLID is party to a Memorandum of Understanding with CAFRAD which is also relevant to accreditation. CAFRAD, an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 by African and Indian Ocean governments, with the support of UNESCO. CAFRAD's Member States are Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Morocco, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Sao Tome & Principe, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Swaziland, Togo and Tunisia. CAFRAD is a partner IGO of the United Nations Public Administration Network (UNPAN). On the topic of mutual accreditation between the two intergovernmental bodies, the MOU (Article 4: Mutual Accreditation) states that "CAFRAD recognizes the governmental and intergovernmental accreditation of EUCLID’s program granted by the Ministries of Education of the EUCLID Participating Parties."
EUCLID / CAFRAD Agreement 

 Regarding ECOWAS and ICCI: Regarding ECOWAS and ICCI:

Please refer to the special pages for more information (ICCI | ECOWAS).
The agreement with ICCI states:
"In order to ensure the international usefulness of the educational programs offered, ICCI recognizes and endorses the governmental and multi- governmental charters and accreditations granted to EUCLID (Article I of constitutive intergovernmental agreement) as well as to the Euclid Consortium, and therefore to EUCLID degrees and certificates."
The agreement with ECOWAS states:
"AWARE of the curriculum and syllabus of EUCLID degree programmes and of the necessity to promote international recognition for African programmes in many OECD countries; ALSO AWARE of the governmental and multi-governmental accreditations of EUCLID as an inter governmental educational framework and therefore of all EUCLID-organized joint degrees and certificates..."

Please note that EUCLID (Euclid University) is connected with but not identical with the Euclid Consortium. Please refer to the Consortium site for more information on the accreditation applicable to the consortium's offering.

 MORE INFORMATION ON ACCREDITATION, RECOGNITION AND TRANSFERABILITY MORE INFORMATION ON ACCREDITATION, RECOGNITION AND TRANSFERABILITY
EUCLID, together with the Euclid Consortium, has a mission to serve students from the four corners of the world, which makes the question of global accreditation, recognition and transferability both extremely important and complex.
Accreditation is the formal recognition of an institution or degree program by a governmental agency, or by an independent agency whose judgment is recognized by a government. In most countries, universities are considered government institutions and their degrees are issued under the direct authority of their Ministry of Education.
Ultimately, it must be stressed that acceptance of any academic title by another university or institution is always decided by the receiving institution and cannot be guaranteed or demanded except when treaties in force apply.
|